Fluid proprieties#
Basic proprieties of fluid#
The domain used for the different phases must be defined by a medium characterized by one or more
fluid subdomains of different properties. This composite environment is defined by
Milieu_composite. The models aims to give the basic proprieties of fluids such as:
Kinematic viscosity \(\mu\)
Density \(\rho\)
Thermal diffusivity \(\alpha\)
Conductivity \(\lambda\)
Calorific capacity \(Cp\)
Thermal dilatation coefficient \(\beta_{co}\)
The model is implemented in Fluide_reel_base as
void Fluide_reel_base::set_param(Param& param)
{
param.ajouter("T_ref", &T_ref_);
param.ajouter("P_ref", &P_ref_);
set_additional_params(param);
}
The fluid proprieties operator must fill following tabs:
rho_densitydP_ rho_density derivative regarding pressuredT_ rho_density derivative regarding temperatureh_enthalpydP_ h_enthalpy derivative regarding pressuredT_ h_enthalpy derivative regarding temperaturecp_heat capacitybeta_thermal dilatation coefficientmu_kinematic viscositylambda_conductivity
Non-compressible fluid#
The model is implemented in Fluide_Incompressible (from TRUST incompressible):
void Fluide_Incompressible::set_param(Param& param)
{
Fluide_base::set_param(param);
//La lecture de rho est rendue obligatoire ici
param.supprimer("rho");
param.ajouter("rho",&rho,Param::REQUIRED);
}
This class allows to give the proprieties previously introduced (or are set to \(0\)) but with a density that is mandatory.
Let’s notice that here neither the density nor the specific heat can be a Champ_Uniforme.
Sodium gas#
The model is implemented in Fluide_sodium_gaz:
void Fluide_sodium_gaz::set_param(Param& param)
The model implemented reads Lois_sodium.h and writes:
{ “temperature”, { 371 - 273.15, 2503.7 - 273.15 } }, //Tri-critical point temperature { “pression”, { 4.127e-6, 260e5 } }; // Associated pressure
Sodium liquid#
The model is implemented in Fluide_sodium_liquide:
void Fluide_sodium_liquide::set_param(Param& param)
The model implemented reads Lois_sodium.h and writes:
{ “temperature”, { 371 - 273.15, 2503.7 - 273.15 } }; //de la temperature de solidification au pt tricritique
Stiffened gas#
The model is implemented in Fluide_stiffened_gas:
void Fluide_stiffened_gas::set_param(Param& param)
{
Fluide_reel_base::readOn(is);
if (Cv_ == -1.) Cv_ = R_ / (gamma_ - 1.0);
return is;
}
void Fluide_stiffened_gas::set_param(Param& param)
{
Fluide_reel_base::set_param(param);
param.ajouter("gamma",&gamma_); // Heat ratio
param.ajouter("pinf",&pinf_); // Reference pressure in law
param.ajouter("mu",&mu__); // viscosity
param.ajouter("lambda",&lambda__); // conductivity
param.ajouter("Cv",&Cv_); // heat capacity
param.ajouter("q",&q_);
param.ajouter("q_prim",&q_prim_);
}
The model implemented is:
rho_\(=\frac{p+\texttt{pinf_}}{\left(\texttt{gamma_} -1.0\right)\left(T+273.15\right)\texttt{Cv_}}\), the densitydP_ rho_\(=\frac{1.0}{\left(\texttt{gamma_} -1.0\right)\left(T+273.15\right)\left(\texttt{Cv_} \right)}\), the density derivative regarding pressuredT_ rho_\( =-\frac{p+\texttt{pinf_}}{\left(\texttt{gamma_} - 1.0\right)\left(T+273.15\right)^2\texttt{Cv_}}\), the density derivative regarding temperatureh_\(=\texttt{ gamma_ Cv_}\left(T+273.15\right)+\texttt{q_}\), the enthalpydP_ h_\(=0.\), the enthalpy derivative regarding pressuredT_ h_\( = \texttt{cp_} \left(T,P\right)\), the enthalpy derivative regarding temperaturecp_\( = \texttt{gamma_ Cv_}\), the heat capacitybeta_\( = \frac{1.0}{T+273.15}\)mu_\( = \texttt{mu_ _}\)lambda_\( = \texttt{lambda_ _}\)
R12_C1 and Eau_c3#
The models are implemented in Fluide_R12_c1_liquide, Fluide_R12_c1_gaz,
Fluide_eau_c3_liquide and Fluide_eau_c3_gaz. The low boiling of refrigerant
R12 (dichlorodifluoromethane) mimics Pressurized water reactor dimensionless numbers. Those values
are available in Cathare code. For example, in Krepper and Rzehak [KR11], one can find:
Fluid |
Water |
R12 |
|---|---|---|
Pressure [bar] |
\(155\) |
\(26\) |
\(T_{sat}\) [\textdegree C] |
\(344.9\) |
\(86.5\) |
\(\rho_{liquid}\) [kg/m3] |
\(594.4\) |
\(1019.3\) |
\(Cp_{liquid}\) [kJ/kg] |
\(8.950\) |
\(1.413\) |
\(\lambda_{liquid}\) [W/m/K] |
\(0.472\) |
\(0.0458\) |
\(\mu_{liquid}\) [W/m/K] |
\(6.82 \times 10^{-5}\) |
\(9.23 \times 10^{-5}\) |
\(\rho_{steam}\) [kg/m3] |
\(101.9\) |
\(170.7\) |
\(Cp_{steam}\) [kJ/kg] |
\(14.0\) |
\(1.281\) |
\(\lambda_{steam}\) [W/m/K] |
\(0.126\) |
\(0.0175\) |
\(\mu_{steam}\) [W/m/K] |
\(2.30 \times 10^{-5}\) |
\(1.57 \times 10^{-5} \) |
\(\sigma\) [J/m2] |
\(4.65 \times 10^{-3}\) |
\(1.80 \times 10^{-3}\) |
\(L_{vap}\) [kJ/kg] |
\(966.2\) |
\(86.48\) |
MUSIG fluid and medium#
In homogeneous MUlti-SIze Group (MUSIG), a distribution of bubbles or droplets between \(r_{min}\) and \(r_{max}\) is characterized by a statistical law (linear, exponential or log) and its discretization in \(n\) sub groups with the same velocity, as depicted in Figure 3 from Cheung et al. [CYT08].
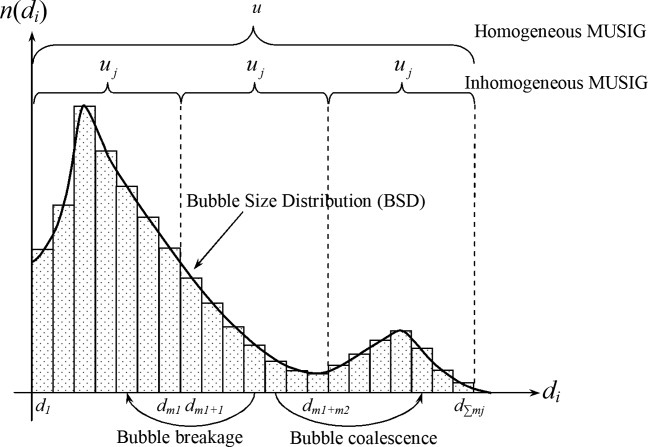
Figure 3 Schema of the standard MUSIG and i-MUSIG models. In MUSIG, all size groups move with the same velocity field, whereas i-MUSIG displays an arbitrary number of velocity groups.#
All bubbles from sub groups share the same velocity as the velocity of the mean Sauter diameter of the distribution \(D_{sm}\). Thus, they share the same common total void fraction equation (mass), velocity (momentum equation) and temperature, allowing to compute only one common set of equations (mass, momentum and energy) with new source terms linked to the changes in the distribution (dilatability, coalescence, break-up).
The model is implemented in Fluide_MUSIG and Milieu_MUSIG:
void Fluide_MUSIG::set_param(Param& param)
{
if(Motcle(mot) == "NBPHASES")
if (Motcle(mot) == "RMIN")
if (Motcle(mot) == "RMAX")
if(Motcle(mot) == "DIAMETRES" || Motcle(mot) == "DIAMETERS")
if (Motcle(mot) == "LIN")
{
repartionType=0;
}
if (Motcle(mot) == "EXP")
{
repartionType=1;
}
if (Motcle(mot) == "LOG")
{
repartionType=2;
}
}
Default value:
\(\texttt{nbSubPhases_} = -1\),
\(\texttt{rMin}=-1\),
\(r\texttt{Max}=-1\).
Example of data set to perform MUSIG computation:
Milieu_MUSIG
{
gaz_helium FLUIDE_MUSIG
{
fluide StiffenedGas { gamma 1.4 pinf 0.0 }
nbPhases 4
diametres { rmin 0.01 rmax 0.1 lin }
}
liquide_sodium FLUIDE_MUSIG
{
fluide StiffenedGas { gamma 4.4 pinf 6e8 }
nbPhases 8
}
}
Interfacial proprieties#
The liquid-gas interface can be characterized by the surface tension \(\sigma\).
The model is implemented in Interface_base as
void Interface_base::set_param(Param& param)
{
Param param(que_suis_je());
set_param(param);
param.lire_avec_accolades_depuis(is);
return is;
}
Default values: \texttt{sigma_ _} \(= -1.\)
The interfacial propriety operator must fill sigma_.
Constant surface tension#
The model is implemented in Interface_ sigma_ constant:
void sigma_(const SpanD T, const SpanD P, SpanD res, int ncomp = 1, int ind = 0) const override
{
for (int i =0; i < (int)P.size(); i++)
res[i * ncomp + ind] = sigma__;
}
Saturation proprieties#
The model aims to give the thermal proprieties at saturation conditions. This class inherits from
Interface. The model is implemented in Saturation_ base as
void Saturation_base::set_param(Param& param)
{
Interface_base::set_param(param);
param.ajouter("P_ref", &P_ref_);
param.ajouter("T_ref", &T_ref_);
}
The saturation proprieties operator must fill following tabs:
Tsat: saturation temperaturedP_Tsat: saturation temperature derivative regarding pressurePsat: saturation pressuredT_ Psat: saturation pressure derivative regarding temperatureLvap: phase change enthalpydP_Lvap: phase change enthalpy regarding pressureHls: enthalpy of liquid phase at saturationdP_Hls: derivative of enthalpy of liquid phase at saturation regarding pressureHvs: enthalpy of steam phase at saturationdP_Hvs: derivative of enthalpy of steam phase at saturation regarding pressure
{\color{red} Warning}: We suppose that we have a unique pressure field to compute it.
Constant saturation proprieties#
The model is implemented in Saturation_constant:
void Saturation_constant::set_param(Param& param)
{
Param param(que_suis_je());
param.ajouter("Tsat", &tsat_,Param::REQUIRED); // Temperature at saturation
param.ajouter("Psat", &psat_,Param::REQUIRED); //Pressure at saturation
param.ajouter("Lvap", &lvap_); // Phase change enthalpy
param.ajouter("Hlsat", &hls_); // Enthalpy of liquid phase at saturation
param.ajouter("Hvsat", &hvs_); // Enthalpy of steam phase at saturation
param.ajouter("tension_superficielle", &sigma__); // Surface tension
param.lire_avec_accolades_depuis(is);
// verifications hlsat/hvsat/lvap
const int i = (lvap_ > 0) + (hls_ > 0) + (hvs_ > 0);
if (i != 2) Process::exit(que_suis_je() + " Please give 2 properties among {Lvap, Hlsat, Hvsat}");
if (lvap_ > 0 && hls_ > 0) hvs_ = hls_ + lvap_;
else if (lvap_ > 0 && hvs_ > 0) hls_ = hvs_ - lvap_;
else if (hls_ > 0 && hvs_ > 0) lvap_ = hvs_ - hls_;
else Process::exit(que_suis_je() + "bad parameters");
return is;
}
The model implemented is:
\(T_{sat} = \texttt{tsat_}\)
\(\frac{D T_{sat}}{Dp} = 0\)
\(P_{sat} = \texttt{psat_}\)
\(\frac{D p_{sat}}{DT} =0\)
\(L_{vap} = \texttt{lvap_}\)
\(\frac{D L_{vap}}{Dp} = 0\)
\(H_{ls} = \texttt{hls__}\)
\(\frac{D H_{ls}}{Dp} = 0\)
\(H_{vs} = \texttt{hvs__}\)
\(\frac{D H_{vs}}{Dp} = 0\)
\(\texttt{sigma_} =\texttt{sigma__}\)
Sodium saturation proprieties#
The model is implemented in Saturation_sodium:
void Saturation_sodium::set_param(Param& param)
{
return Saturation_base::readOn(is);
}
Fluid proprieties from external software#
In this section, the management of fluid properties through an external software is described. One can use EOS, the CEA-EDF software for state equation management (section xx), or CoolProp, an open-source alternative. Both EOS and CoolProp can call the NIST state equation software named Refprop. EOS can use a user-defined state equation through a plugin. CoolProp provides free state equations for a selected list of fluids (available here).
Basic proprieties of fluid with TPPI#
The generic table of proprieties from external software is implemented in Fluide_generique_TPPI_base:
void Fluide_generique_TPPI_base::set_param(Param& param)
#
if (tmax_ < -100. )
return Fluide_reel_base::unknown_range();
return { { "temperature", { tmin_ - 273.15, tmax_ - 273.15 } }, { "pression", { pmin_, pmax_ } } };
}
Default values:
\(tmin_ = -123.\),
\(tmax_ = -123.\),
\(pmin_ = -123.\),
\(pmax_ = -123.\)
and
rho_: densitydP_rho_: density derivative regarding pressuredT_rho_: density derivative regarding temperatureh_: enthalpydP_h_: enthalpy derivative regarding pressuredT_h_: enthalpy derivative regarding temperaturecp_: heat capacitybeta_: thermal dilatation coefficientmu_: kinematic viscositylambda_: conductivity
CoolProp#
The model is implemented in Fluide_generique_CoolProp:
void Fluide_generique_CoolProp::set_param(Param& param)
{
param.ajouter("model|modele", &model_name_, Param::REQUIRED);
param.ajouter("fluid|fluide", &fluid_name_, Param::REQUIRED);
TPPI_ = std::make_shared<EOS_to_TRUST_generique>();
TPPI_->set_fluide_generique(model_name_, fluid_name_);
TPPI_->desactivate_handler(false); // throw on error
if (model_name_ == "CATHARE2" || model_name_ == "EOS_CATHARE2")
{
tmin_ = TPPI_->tppi_get_T_min();
tmax_ = TPPI_->tppi_get_T_max();
pmin_ = TPPI_->tppi_get_p_min();
pmax_ = TPPI_->tppi_get_p_max();
}
}
Validity domain for Cathare tables with tmin_, tmax_, pmin_,
pmax_. Accessible here.
EOS#
The model is implemented in Fluide_generique_EOS:
void Fluide_generique_EOS::set_param(Param& param)
{
param.ajouter("model|modele", &model_name_, Param::REQUIRED);
param.ajouter("fluid|fluide", &fluid_name_, Param::REQUIRED);
param.ajouter("phase", &phase_, Param::OPTIONAL); // optional: liquid or vapor. PI: specify the phase it is really useful (better perf for coolprop) !
if (model_name_ == "REFPROP") TPPI_->set_path_refprop();
tmin_ = TPPI_->tppi_get_T_min();
tmax_ = TPPI_->tppi_get_T_max();
pmin_ = TPPI_->tppi_get_p_min();
pmax_ = TPPI_->tppi_get_p_max();
}
Validity domain for Refprop tables with tmin_, tmax_, pmin_, pmax_. Availability of 147 pure
fluids, 5 pseudo-pure fluids (such as air), and mixtures with up to 20 components. Available
here.
For instance, a boiling flow using refprop10 must be specified as
liquide_eau Fluide_generique_EOS { model refprop10 fluid waterliquid }
gaz_eau Fluide_generique_EOS { model refprop10 fluid watervapor }
Saturation proprieties (TPPI)#
The generic table of proprieties from external software is implemented in
Saturation_generique_TPPI_base:
void Saturation_generique_TPPI_base::set_param(Param& param)
The saturation proprieties operator must fill following tabs:
Tsat: saturation temperaturedP_Tsat: saturation temperature derivative regarding pressurePsat: saturation pressuredT_Psat: saturation pressure derivative regarding temperatureLvap: phase change enthalpydP_Lvap: phase change enthalpy regarding pressureHls: enthalpy of liquid phase at saturationdP_Hls: derivative of enthalpy of liquid phase at saturation regarding pressureHvs: enthalpy of steam phase at saturationdP_Hvs: derivative of enthalpy of steam phase at saturation regarding pressure
CoolProp (TPPI)#
The model is implemented in Fluide_generique_CoolProp:
void Fluide_generique_CoolProp::set_param(Param& param)
{
if (model_name_ == "REFPROP") TPPI_->set_path_refprop();
param.ajouter("model|modele", &model_name_, Param::REQUIRED);
param.ajouter("fluid|fluide", &fluid_name_, Param::REQUIRED);
param.ajouter("phase", &phase_, Param::OPTIONAL); // optional: liquid or vapor. PI: specify the phase it is really useful (better perf for coolprop) !
param.ajouter("sigma_mano", &sigma_mano_, Param::OPTIONAL); // optional: because of issues when we call surface tension in TTSE in coolprop ! Try without and if calculation doesn't pass, input sigma
}
Default value: \(\texttt{sigma_mano_}=-1.\)
EOS (TPPI)#
The model is implemented in Fluide_generique_CoolProp:
void Fluide_generique_CoolProp::set_param(Param& param)
{
TPPI_ = std::make_shared<EOS_to_TRUST_Sat_generique>();
param.ajouter("model|modele", &model_name_, Param::REQUIRED);
param.ajouter("fluid|fluide", &fluid_name_, Param::REQUIRED);
param.ajouter("sigma_mano", &sigma_mano_, Param::OPTIONAL); // optional: because of issues when we call surface tension in TTSE in coolprop ! Try without and if calculation doesn't pass, input sigma
}
Default value: \(\texttt{sigma_mano_}=-1.\)
For example:
saturation_eau saturation_generique_EOS { model refprop10 fluid waterliquid }
